Real estate valuation is the process of determining what a property is worth at a specific moment in time. Valuations are also used by stakeholders in real estate, including buyers, sellers, mortgage lenders, investors and home insurance companies.
But when we think of terms commonly used to assess the worth of a piece of property (value, cost and price) how are those figures actually determined? How is value assessed, and what calculations are used to guide and govern real estate transactions?
Let’s take a look at the factors that can impact a real estate valuation, the three main real estate valuation methods and how they’re calculated.
What Does Valuation Mean In Real Estate?
A real estate valuation is a formal assessment of the value of a property and can serve a variety of needs in the real estate ecosystem, from securing a mortgage as a first-time home buyer to refinancing your home years later. There are several types of valuation used in different scenarios depending on the purpose of the valuation.
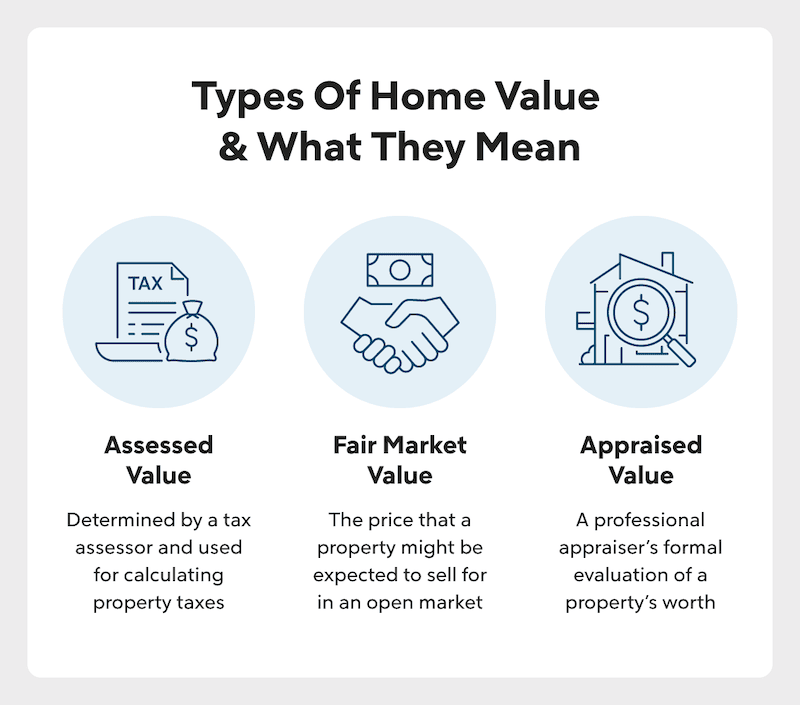
There are three types of value in real estate that are commonly used for assessing property: assessed value, fair market value and appraised value. Here’s what they mean and how they differ:
- Assessed value: Generally used for tax purposes, a home’s assessed value is determined by a municipal or county tax assessor, depending on your location. The higher your assessed value, the higher your property taxes will be.
- Fair market value: This value is defined as the price that a property might be expected to sell for in an open market between a willing buyer and a willing seller with reasonable knowledge of the property.
- Appraised value: This type of value is a professional appraiser’s formal evaluation of a property’s worth, which considers a number of factors that impact value. An appraisal informs what a buyer might expect to pay and what a lender is willing to lend for a property.
See What You Qualify For
Buy A Home
Discover mortgage options that fit your unique financial needs.

Refinance
Refinance your mortgage to have more money for what matters.
Tap Into Equity
Use your home’s equity and unlock cash to achieve your goals.
Real Estate Valuation Methods
When it comes to formal assessments of residential properties, there are three core methods of valuation in real estate, which each have different calculation models. Each method is typically conducted by a licensed appraiser, property valuer or surveyor:
- Sales comparison approach
- Cost approach
- Income valuation approach
While these three are the most common for residential properties, it should be noted that other methods can be used for commercial and industrial properties, such as the value-per-door approach or the cost-per-rentable square foot approach.
1. Sales Comparison Approach
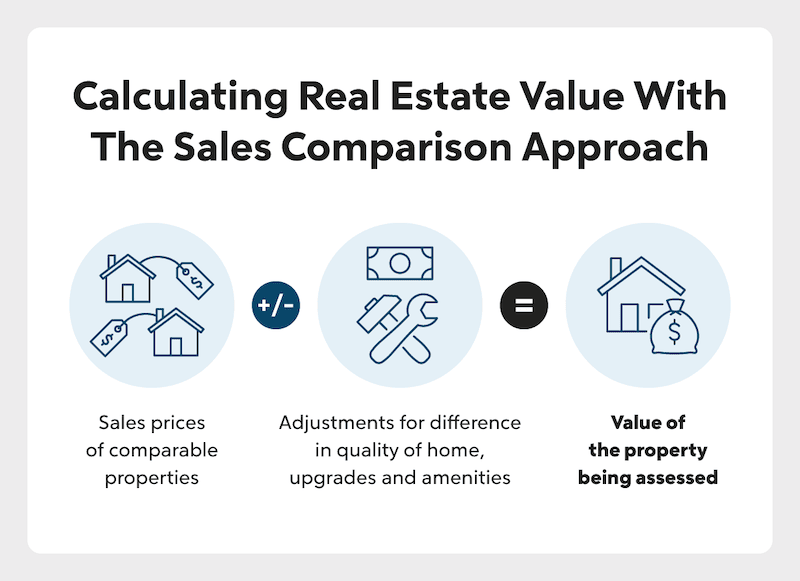
One of the most popular valuation methods is the sales comparison approach. In this model, an appraiser cites recently sold properties to justify the valuation of a home of commensurate size and quality. Using this method, the value of the property being assessed is based on the sales prices of comparable homes, adding or subtracting value for any adjustments.
For example, let’s say you’re comparing a 2,000-square-foot colonial-style home to a home of similar construction and size, but the comparable home’s features are upgraded. Significant upgrades to the kitchen like new appliances or custom cabinetry impact the value of the home. So, the colonial-style home under assessment might be valued lower than the comparable house based on the difference in the value of those upgrades.
The most common factors in the sales comparison approach are:
- Location and neighborhood
- Recently sold listings
- Amenities and updates
- Age and condition
- Average price per square foot
2. Cost Approach
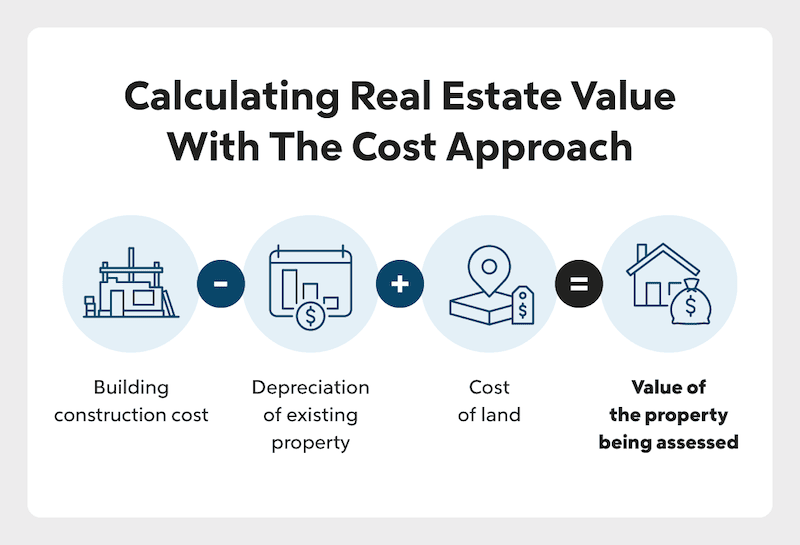
The second of three valuation methods is the cost approach, which is based on construction costs of building a similar home, while accounting for land value and depreciation. In the cost approach, a home’s valuation is calculated by estimating what it would cost to build a net new property of comparable size and quality from the ground up. Within this approach, there are two variations in methodology:
- Replacement method: Calculates the cost of constructing the same home with modern materials and methods of construction.
- Reproduction method: Calculates the cost of duplicating the exact home with materials and methods of construction contemporary to the home’s original era (materials and methods available in the 1960s, if the home was originally constructed in the 1960s).
Either of these two methods of determining replacement value can be used for valuation in the cost approach.
3. Income Capitalization Approach
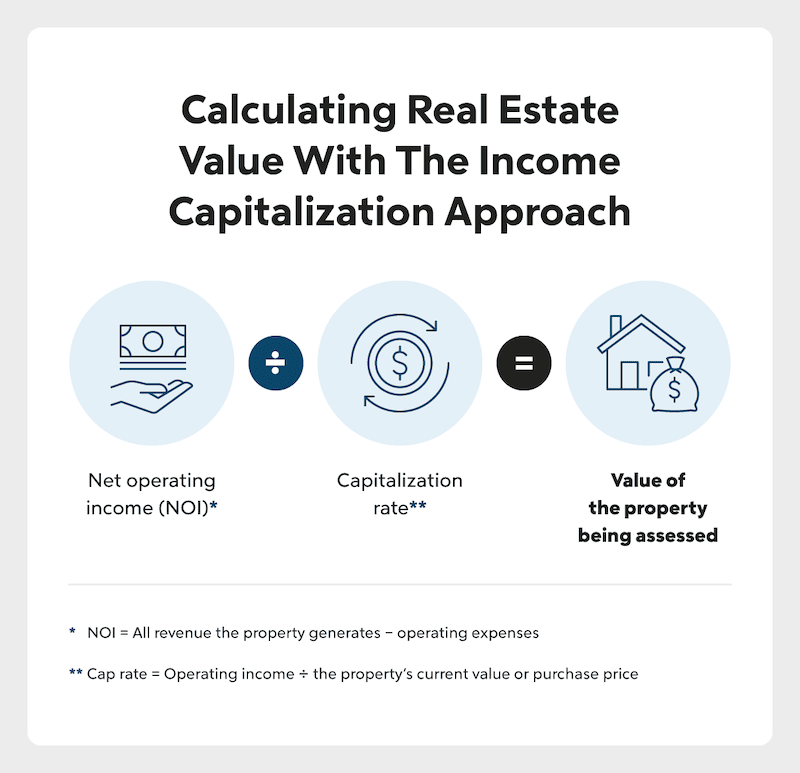
The third valuation method for residential property is the income capitalization approach, also known as the income approach. This method is typically used for assessing investment or rental properties, such as vacation homes or apartment buildings, which are generally acquired to produce a return on investment.
The income capitalization approach is calculated by assigning a value to a property based on the estimated returns that property has the potential to produce. A property’s estimated returns are determined by dividing the property’s net operating income (NOI) by the capitalization rate.
Let’s take a closer look at NOI and capitalization rate.
Net Operating Income (NOI)
Net operating income is determined by taking the value of revenue generated by the property and subtracting any operating expenses such as taxes, maintenance and repairs and insurance fees.
For example, if an investment property is rented at $2,000 per month, it has the potential to generate $24,000 per year. If the sum of operating expenses for that same property comes to $7,500 (assuming $3,000 in annual property taxes, $1,500 in annual insurance fees and $3,000 in unexpected repair costs), then your net operating income would be $16,500.
Capitalization Rate
Capitalization rate, also known as cap rate, is the expected rate of return on a property. It’s determined by dividing net operating income by the property’s current value or purchase price.
Which Real Estate Valuation Is Most Accurate?
There are several approaches to real estate valuation for good reason: Each provides an accurate look at value for different use cases.
The best method for valuing residential property is usually the sales comparison method. It’s looked to as an accurate representation of residential property value because it first reviews recent, comparable sales in the area most similar to the subject property. It then provides a qualitative assessment of the property’s physical attributes in conjunction with broader market activity, including:
- Location
- Property age
- Interior and exterior condition
- Market conditions at the time of sale
What Is The Most Popular Valuation Method?
The most popular valuation method for residential real estate is also the sales comparison method, which determines value based on comparable, recent sales local to the subject property.
It is rarer to find the cost approach in residential real estate valuations, though use cases do exist. Similarly, the income approach is typically reserved for rental and investment properties but is not used as commonly as the sales comparison method.
Is A Valuation The Same As An Appraisal?
Though both the term valuation and the term appraisal refer to ways of judging a property’s worth, they are not exactly the same. A valuation is the assessment of a specific property’s worth at a specific moment in time, which can be used for legal, financial or transactive purposes.
An appraisal is the formal process through which an estimate or opinion of a property’s value is determined, using one of three core methods: the sales comparison, cost or income capitalization approach. An appraisal is provided through a written report that details the factors that contributed to the resulting valuation of a property. Appraisals are a service provided by a licensed professional in exchange for a fee.
Real Estate Valuation FAQs
Let’s take a look at some frequently asked questions about property valuation.
What is a property valuation used for?
A property valuation is most commonly used for determining the fair market value of a property. Other common uses for a real estate valuation include:
- Financing
- Investment analysis
- Property insurance
- Property taxes
How is assessed value different from appraised value?
If you’re looking at assessed value versus appraised value, there are a few differences. An assessment is generally used to determine property value for income tax purposes and is determined by a tax assessor. In contrast, the appraised value is determined by a professional appraiser and is used primarily by buyers, sellers and lenders during real estate transactions.
Do market conditions affect real estate valuation?
Yes, the current real estate market conditions will have an effect on the value of your property with any of the three valuation methods. No matter what method you use, the current market impacts how much your home is worth at a fixed point in time.
The Bottom Line
Real estate valuations are a vital part of the residential property ecosystem, providing a single source of truth for buyers, sellers, mortgage lenders, real estate investors and home insurance companies alike.
Understanding the key factors and calculations that determine the value of your home can help you prepare for the future, like considering ways to increase the value of your home now before you prepare to sell, or estimate valuation yourself so there are no surprises when your formal assessment arrives.
Ready to refinance?
See recommended refinance options and customize them to fit your budget.

Victoria Araj
Victoria Araj is a Staff Writer for Rocket Companies who has held roles in mortgage banking, public relations and more in her 15-plus years of experience. She has a bachelor’s degree in journalism with an emphasis in political science from Michigan State University, and a master’s degree in public administration from the University of Michigan.












