A Helpful Guide To Home Improvement Loans

No matter how much you love your home, there are probably things you want to change about it. Whether it’s refreshing an outdated bathroom or making the house more functional for your growing family, a house renovation can give you the home you want.
But making changes to your house can be expensive, and not everyone has the cash on hand. If you find yourself in this situation, home improvement loans can help. But anytime you’re borrowing money, it’s essential to research the best terms for your situation.
What Is A Home Improvement Loan?
A home improvement loan is money you borrow to pay for a home improvement project. A home improvement project can cover anything from minor repairs to major renovations. For example, you could use a home improvement loan to repaint your house, remodel your kitchen or make structural changes to your home.
These loans can be secured or unsecured, depending on your lender and financial situation. And there are many different types of financing you can choose from, like a personal loan, home equity line of credit (HELOC) or a home equity loan.
See What You Qualify For
Home Purchase
Home Refinance
Tap Into Equity
How Do Home Improvement Loans Work?
Home improvement loans require the homeowner to borrow money and pay it over time. Your interest rate and financing terms will vary depending on the following factors.
Secured Debt Vs. Unsecured Debt
Financing generally falls into two different categories: secured and unsecured debt. An unsecured loan has no collateral requirements and is issued solely based on the borrower’s credit history.
Unsecured debt is riskier for the lender because, if you default on the loan, they’ll have to issue a lawsuit to collect on the debt. For that reason, unsecured loans tend to come with higher interest rates.
A secured loan is backed by some type of collateral. For example, a mortgage is a secured loan because, if you default, the lender can repossess the home. Since these loans are less risky for the lender, they come with lower interest rates.
Fixed Payments Vs. Revolving Credit
When you’re taking out a home improvement loan, you can choose between installment loans or revolving credit. Installment loans are distributed as a lump sum of money and repaid in fixed monthly payments.
Once the loan is repaid in full, your account is considered closed. A cash-out refinance, home equity loan and personal loan are all forms of installment loans. These loans tend to come with low rates and flexible monthly terms.
In comparison, a revolving credit account gives you access to an ongoing line of credit. The account is never truly closed because you can borrow from the line of credit as needed. Credit cards and HELOCs are good examples of revolving credit.
When it comes to home improvement projects, you can choose either type of financing. An installment loan is a better option if you know exactly how much money you need. Whereas a revolving credit line is better for homeowners whose financing needs fluctuate.
Use Your Home Equity To Finance Home Improvements
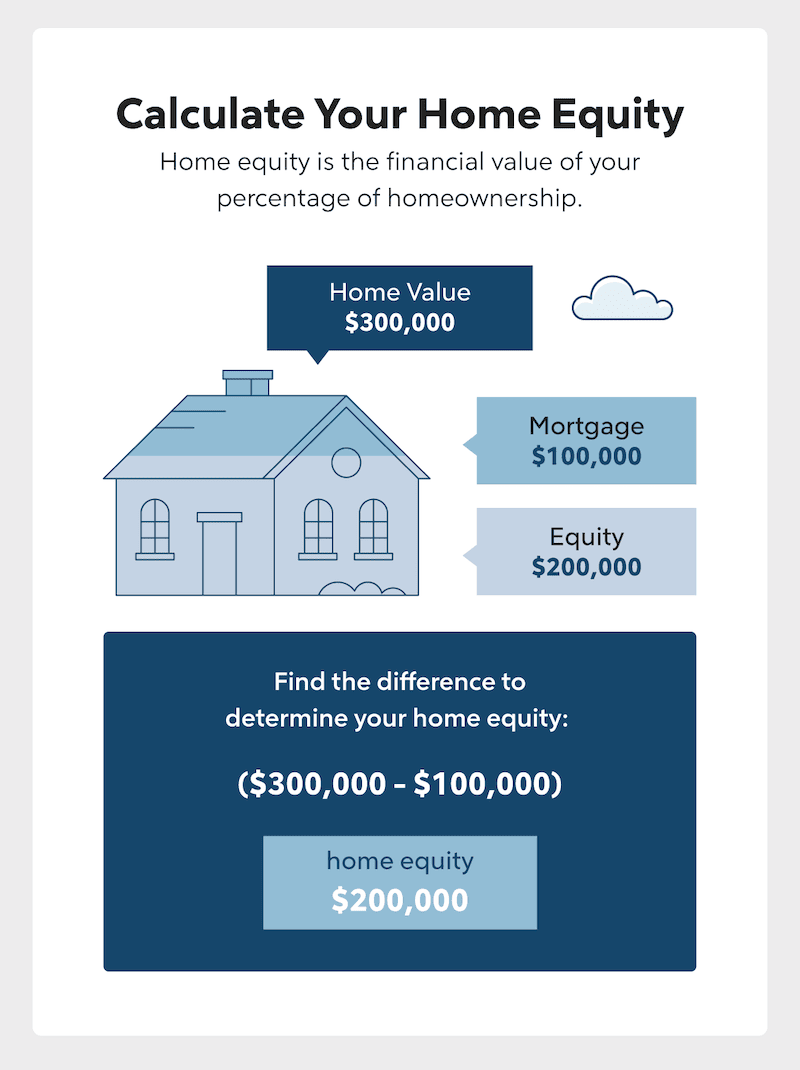
As a homeowner, you have the option to tap into your home’s equity and use it to pay for improvements to your house. Home equity is the difference between what you owe on your home and what it’s currently worth.
For example, if you owe $200,000 on your home and your home is worth $300,000, you have access to $100,000 in equity. Listed below are three ways you can use your equity to pay for home renovations.
Cash-Out Refinance
If the interest rate on your mortgage is higher than the current market rates, you might consider a cash-out refinance. You’ll refinance your existing mortgage for an amount that’s more than what you currently owe and receive the difference in cash.
A cash-out refinance is a good way to earn more favorable rates and terms on your loan. It’ll also give you the money you need to pay for your home improvements without taking out a separate loan.
But if current market rates are higher than your loan terms, a cash-out refinance might not be the best option for you. While you’ll be able to access your home equity, you’d have to pay more interest on your mortgage for the remainder of your loan term.
Home Equity Loans
A home equity loan is often referred to as a second mortgage. When you take out a loan, the funds are secured by the equity in your home. Home equity loans can be used for any purpose, including renovations or repairs.
Depending on your credit score and financial situation, you can take out a loan for up to 90% of your home’s equity. A home equity loan will come with interest rates that are higher than your mortgage but will still be more affordable than taking out an unsecured personal loan. Because the loan is a second mortgage, you’ll have two mortgage payments.
You can also deduct your mortgage interest on a second mortgage if the funds are used for home improvements. So this could help you save some extra money come tax season.
Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC)
A home equity line of credit (HELOC) allows you to borrow money using your home’s equity as collateral. Your lender will set a borrowing limit, and you can take as much money from the line as you need.
You can repay what you borrowed and borrow again during the draw period, which typically lasts 10 years. During the draw period, you only pay interest on the equity you use. You’re only required to pay something toward the principal once the draw period ends.
If you’re considering an extensive renovation and aren’t totally sure how much it will cost, a HELOC might be a good option for you. For example, if you decide to redo your kitchen, a contractor may quote you an initial estimate of $10,000. But as time goes on, you may run into issues with repairs or decide on different cabinetry. A $10,000 estimate could easily double in this case, and a HELOC’s flexibility allows you to borrow as needed.
Fund your renovations with a cash-out refinance.
See what you qualify for!
Pros And Cons Of Using Home Equity For Home Improvement
There are many advantages to using your home equity to pay for a home improvement project, but there are drawbacks to consider.
Pros
- Lower interest rates: Because the financing is secured by the equity in your home, it’s less risky for your lender. That means you’ll secure lower interest rates than you’d receive on an unsecured personal loan.
- Potential to borrow more: If you’ve built up a lot of equity in your home, you may be able to borrow more money than you’d be approved for otherwise.
- Income tax deduction: If you take out a second mortgage and use the funds to pay for home repairs, you can deduct the interest paid on your taxes.
Cons
- Your home is at risk: If you’re unable to make the payments on your loan, the bank can foreclose on your home.
- Need good credit: Home equity loans come with more stringent credit requirements, and borrowers with poor credit may not qualify.
- Longer process: A home equity loan may not be the best option if you need the money immediately. The application and approval process usually takes longer than a personal loan.
- Application fees: Your lender may charge application or origination fees on the loan.
Take Advantage Of Government-Backed Home Renovation Loans
If you don’t want to use your home equity to finance a home improvement project, you might consider applying for a government-backed loan. These loans tend to be easier to qualify for, so they’re a good option for borrowers with less than perfect credit.
FHA 203(k) Loans
An FHA 203(k) loan allows you to finance major and minor home improvement projects. These loans are backed by the FHA, so you can qualify with a credit score of at least 580. However, the total property value can’t fall below the FHA’s local limits.
VA Renovation Loans
VA renovation loans or VA cash-out refinance can be used by eligible veterans, current service members and surviving spouses to finance a home renovation project. The maximum loan amount is determined based on the home’s value and equity. And borrowers must provide their lender with a certificate of eligibility (COE).
Home Improvement Grants
Home improvement grants offered at the state, government and local levels can be used to finance home improvement projects. For example, the USDA’s Section 504 Home Repair Program offers grants and loans to low-income homeowners looking to improve their homes.
Like the government loans available, these grants typically have strict qualifications for approval. You may qualify for a grant if you belong to one of the following groups:
- Low and very-low-income families
- Senior citizens
- Homeowners with disabilities
- Active military service members and veterans
- Native and indigenous groups in America
Be sure to explore local community-based organizations as well. Many large cities have housing organizations and volunteer groups to provide funding or labor for home renovations, especially if health and safety are a concern.
Pros And Cons Of Using Government Loans For Home Improvement
Listed below are the biggest advantages and disadvantages of using government loans for a home improvement project.
Pros
- Lower credit score requirements: Because these loans are backed by a government agency, they may not be considered as risky to your lender. So these loans are often a good option for borrowers with lower credit scores.
- Lower interest rates: Government-backed loans, like FHA and VA loans, often come with lower interest rates.
Cons
- Need to meet eligibility requirements: Government-backed loans typically target borrowers in a certain demographic, and not everyone will qualify. For example, VA loans are specifically for eligible veterans, active duty service members and their families.
- More complex application process: Government loans often have a more complex application process because you have to prove you meet the eligibility requirements.
Guide to VA Loans
Discover a more affordable loan option for United States Veterans, Service Members and spouses.
Consider Unsecured Debt To Finance Home Improvements
Unsecured debt is another way homeowners can finance home improvements and renovations. This type of financing is easier to qualify for but may come with higher interest rates.
Personal Loans
A personal loan is a loan that’s not backed by any type of collateral. These loans can be used for a variety of purposes, including home improvement projects. Personal loans usually come with fixed interest rates, and your interest rate will depend on your creditworthiness.
You may want to consider a personal loan for home renovations if the project you’re financing is relatively small, and you can pay the loan off within 3 – 7 years. It’s also a good idea for homeowners who don’t have much equity built up.
But if you need to borrow a large sum of money, personal loans may not be the best choice. Personal loans usually have higher rates and shorter loan terms than a second mortgage or cash-out refinance, so your payments may be less affordable.
Contractor Financing
Some contractors are willing to offer financing through a third-party lender during the home renovations. Loan rates and terms will vary based on the contractor and the lender, but you may be able to find loan options without any fees.
Since the financing is project-based, this reduces the likelihood that you’ll borrow more than you need. And you may be able to start on your home renovations sooner since there will be fewer negotiations between the lender and contractor.
Credit Cards
Credit cards usually come with steep interest rates, but they can be a good option for small home upgrades that you can repay before the interest accumulates. If you utilize this option, you may want to try to find a new credit line with 0% APR for the first year. Just keep in mind that applying for new credit can have a negative impact on your credit score and the 0% APR won’t be as beneficial if you don’t pay the card off before the promotional rate ends.
There are benefits to paying with your card, but the interest rates will be significantly higher than other financing options. So you should have the funds to repay the renovation expenses before using a credit card to finance a home improvement project.
Pros And Cons Of Using Unsecured Debt For Home Improvements
Here are some pros and cons of using unsecured debt to pay for home improvements.
Pros
- Faster access to money: Unsecured loans, like personal loans and credit cards, are much easier to qualify for than other types of financing. If you need fast access to the funds, unsecured debt could be an option for you.
- Payment flexibility: These loans often come with flexible repayment terms. For example, if you choose contractor financing, you may be able to negotiate the loan terms with a third-party lender.
Cons
- Higher interest rates: Because unsecured debt is riskier for the lender, this type of financing will always come with higher interest rates.
- Variable rates: Some types of unsecured debt come with variable rates, which means your interest rate will go up and down over the life of the loan.
Get cash now for your next home improvement project.
Getting a personal loan is quick and easy.
How To Get A Home Improvement Loan
Here are five steps you can take to apply and qualify for a home improvement loan.
1. Check Your Credit
Before applying for a home improvement loan, it’s important to check your credit score to determine which type of home improvement loan is best for you. Borrowers with excellent credit will qualify for different loan options than borrowers with bad credit.
2. Check Your Equity
It’s a good idea to see how much equity is available in your home. If you’ve built up a large amount of equity, a home equity loan or cash-out refinance may make the most sense for you.
3. Research Your Options
Researching and receiving quotes from different lenders will help you find the best rates and terms on your loan or line of credit. It’s a good idea to receive quotes from at least three different lenders before making a decision. During the prequalification stage, lenders will do a soft inquiry on your credit, so this shouldn’t hurt your credit score.
4. Submit An Application
Once you’ve settled on a lender, you’ll submit your loan application and move through the underwriting process. The application process will vary depending on the type of loan you’re applying for.
5. Pay Back Your Loan
Once you’ve received the funds, you should be ready to start making payments on your loan immediately. If you aren’t ready to repay your loan, you risk incurring late fees and damaging your credit.
Home Improvement Loan FAQs
There are several options available to finance your home renovations. If you’re looking for the best home improvement loans, below are some additional insights to help you choose.
Can I get a home improvement loan with no equity?
There are several other ways you can cover your home renovations without equity, including a personal loan, using a credit card, or home repair grants. And if you’re looking for a loan with better interest rates, government-backed loans may be a good option.
Are home improvement loans tax deductible?
Home equity loans are tax deductible if you use the funds for home improvements. But most other home improvement loans aren’t tax deductible.
Can I get a home improvement loan with bad credit?
You may have a hard time qualifying for a home equity loan if you have bad credit. Borrowers with poor credit may want to consider government-backed loans or unsecured personal loans.
The Bottom Line
Home improvement projects can be hard on a homeowner’s budget, so many people look into different financing options. If you want to renovate your home in the coming year, you may consider to leverage your existing home equity.
Need extra cash for home improvement?
Use your home equity for cash-out refinance.











